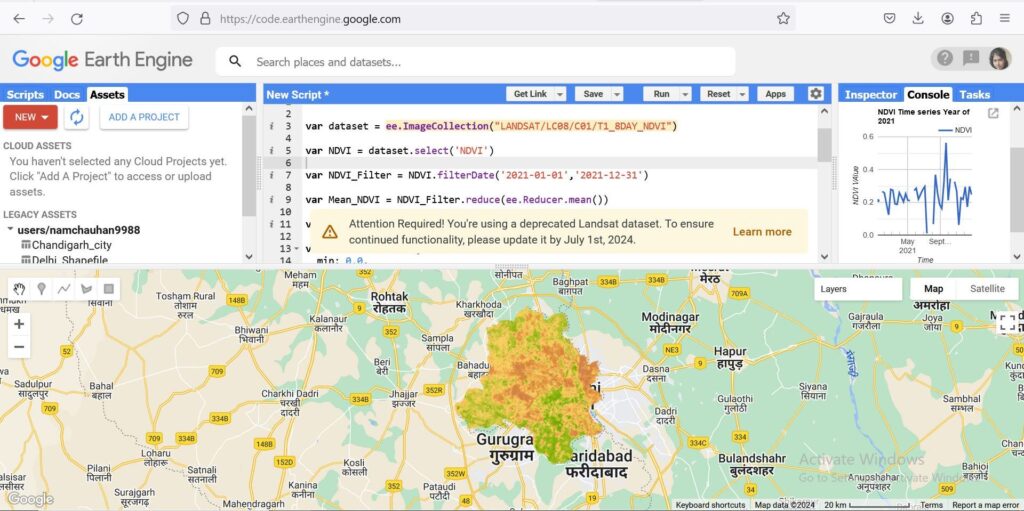
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized how we understand and interact with the world around us. Among the various tools available to GIS professionals and enthusiasts, Google Earth Engine (GEE) stands out as a transformative platform, offering unparalleled capabilities for environmental monitoring, spatial analysis, and decision-making. Here’s why Google Earth Engine is so crucial in the realm of GIS.
1. Massive Data Repository
Google Earth Engine provides access to an extensive archive of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets, including historical data spanning several decades. This wealth of information allows users to analyze changes over time, making it invaluable for research in areas such as climate change, deforestation, urbanization, and disaster management.
2. Cloud-Based Processing Power
One of the significant challenges in GIS is the need for substantial computational resources to process large datasets. GEE’s cloud-based infrastructure eliminates this hurdle by leveraging Google’s powerful servers. Users can perform complex analyses and run sophisticated algorithms without needing high-end local hardware, making advanced GIS accessible to a broader audience.
3. Scalability and Speed
The ability to scale operations quickly is a key advantage of Google Earth Engine. Whether you are analyzing a small area or conducting a global study, GEE can handle the task efficiently. Its cloud infrastructure ensures that even large-scale projects can be completed swiftly, which is critical for timely decision-making in areas like disaster response and environmental monitoring.
4. Integrated Development Environment
Google Earth Engine comes with an integrated development environment (IDE) that supports JavaScript and Python, allowing users to write and execute code directly in their web browser. This feature simplifies the process of developing, sharing, and replicating analyses. The platform also includes a rich library of pre-built functions and tutorials, aiding both novice and experienced users in their work.
5. Collaboration and Sharing
Collaboration is at the heart of modern scientific research and planning. GEE facilitates this by enabling users to share their projects, datasets, and scripts easily. Collaborative projects can span across institutions and countries, fostering a global approach to solving environmental and geographical problems.
6. Real-Time Data and Monitoring
For applications requiring real-time data, such as disaster response or agricultural monitoring, GEE’s ability to ingest and process near real-time satellite imagery is crucial. Users can monitor events as they happen and deploy rapid response measures based on the latest data, enhancing the efficacy of interventions.
7. Environmental and Social Impact
GEE has been instrumental in various high-impact projects around the world. From tracking deforestation in the Amazon rainforest to assessing the impacts of climate change on polar ice caps, the insights gained through GEE have informed policy decisions, conservation efforts, and sustainable development initiatives.
Conclusion – Google Earth Engine
Google Earth Engine is more than just a tool; it is a catalyst for innovation in GIS. Its combination of vast data resources, powerful cloud-based processing, and user-friendly features makes it an indispensable asset for researchers, planners, and policymakers. By democratizing access to advanced geospatial analysis, GEE is playing a crucial role in addressing some of the most pressing environmental and social challenges of our time. Whether you are a seasoned GIS professional or a curious newcomer, exploring the capabilities of Google Earth Engine can open up new horizons in your work and research.