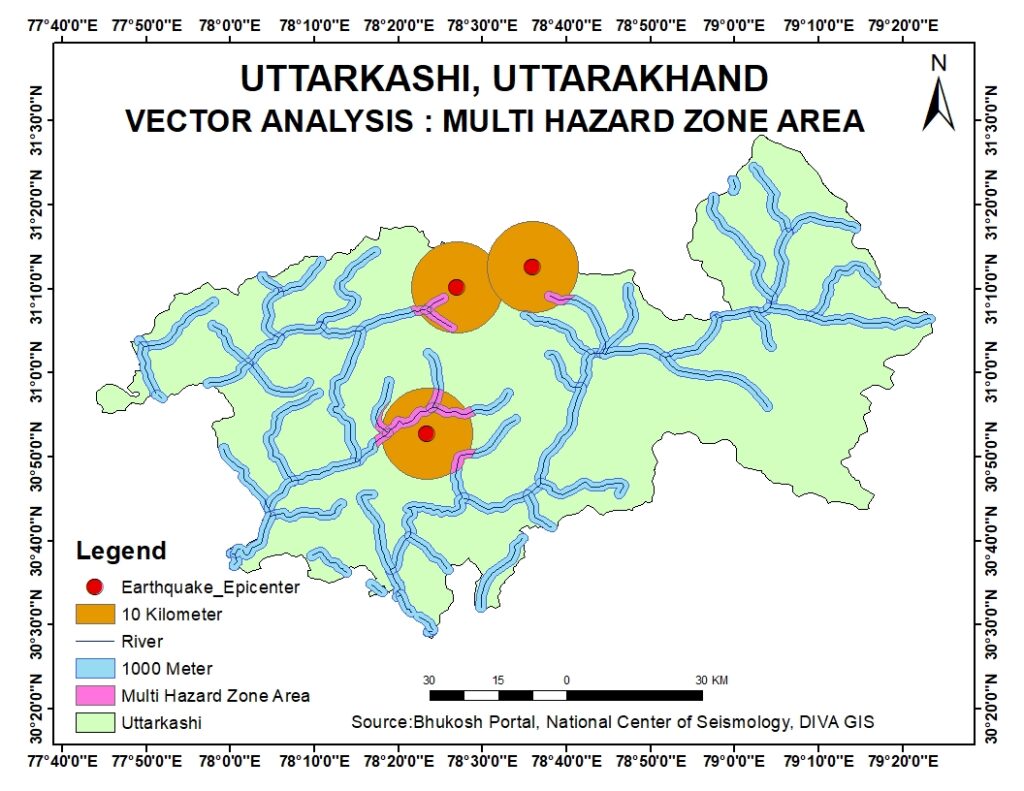
VECTOR ANALYSIS
Single layer analysis techniques include selecting by attributes and calculating new attribute values with the field calculator.
Many vector analysis techniques involve overlaying two or more datasets and using their spatial relationship to alter or create attributes and/or entities.
Vector data analysis uses the geometric objects of point, line, and polygon.
The accuracy of analysis of results depends on the acccuracy of these objects in terms of location and shape.
vector data comprises of individual points stored as coordinate pairs that indicate a physical location in the world.
These points can be joined, in a particular order, to form lines or joined into closed areas to form polygons.
Vector data is extremely useful for storing and representing data that has discrete boundaries, such as borders or building footprints, streets and other transport links, and location points.