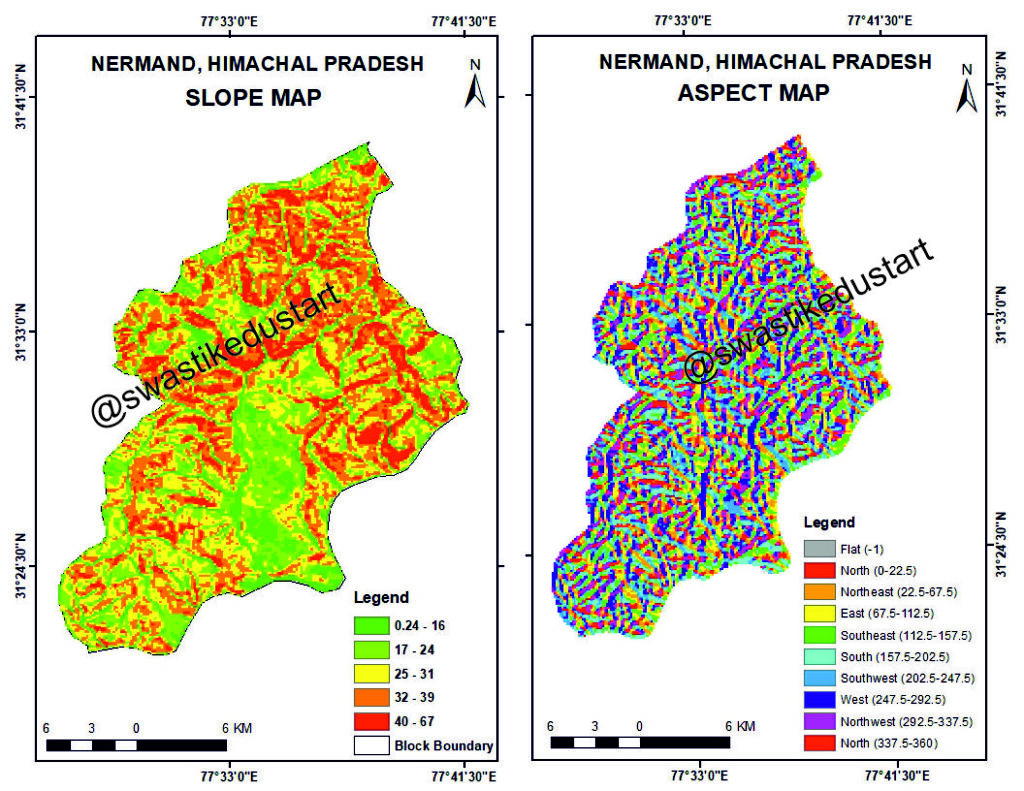
Understanding the Slope and Aspect Map of Nermand, Himachal Pradesh: A Complete GIS-Based Terrain Analysis
Nermand, a picturesque region in Himachal Pradesh, is known for its rugged Himalayan terrain, terraced agriculture, and breathtaking mountain views. But beyond its natural beauty lies a complex topography that plays a crucial role in land-use planning, agriculture, watershed management, and disaster risk assessment. In this blog, we explore the Slope Map and Aspect Map of Nermand, generated using modern GIS and remote sensing techniques.
WHAT IS A SLOPE MAP?
A slope map represents the steepness or gradient of the terrain, calculated from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). Slope values are expressed in degrees.
Slope Categories:
• 0.24–16° (Gentle)
• 17–24° (Moderate)
• 25–31° (Moderately Steep)
• 32–39° (Steep)
• 40–67° (Very Steep)
WHAT THE SLOPE MAP REVEALS
Nermand is dominated by moderate to very steep slopes, typical of the Western Himalayas. Understanding slope is essential for:
• Agriculture
• Urban planning
• Road alignment
• Hydrological modeling
• Hazard mapping
WHAT IS AN ASPECT MAP?
The aspect map shows the direction toward which a slope faces. Aspect affects sunlight exposure, soil moisture, vegetation, climate, and snowmelt.
Aspect Categories Include:
• North
• Northeast
• East
• Southeast
• South
• Southwest
• West
• Northwest
• Flat areas
WHY SLOPE AND ASPECT ANALYSIS MATTERS
1. Land-Use Planning and Infrastructure
2. Agriculture Suitability
3. Disaster Management
4. Watershed and Hydrology Management
HOW THE MAPS WERE CREATED
The maps were created using GIS tools such as QGIS, ArcGIS, and DEM datasets.
CONCLUSION
The Slope Map and Aspect Map of Nermand provide crucial insights into the region’s terrain, supporting better land-use planning, hazard assessment, and environmental management.
HASHTAGS:
#Nermand #HimachalPradesh #SlopeMap #AspectMap #GIS #RemoteSensing #TerrainAnalysis #Himalayas #LandUsePlanning
